“`html
Best 7 Effective Methods for Calculating the Volume of a Triangular Prism
Understanding the Volume of a Triangular Prism
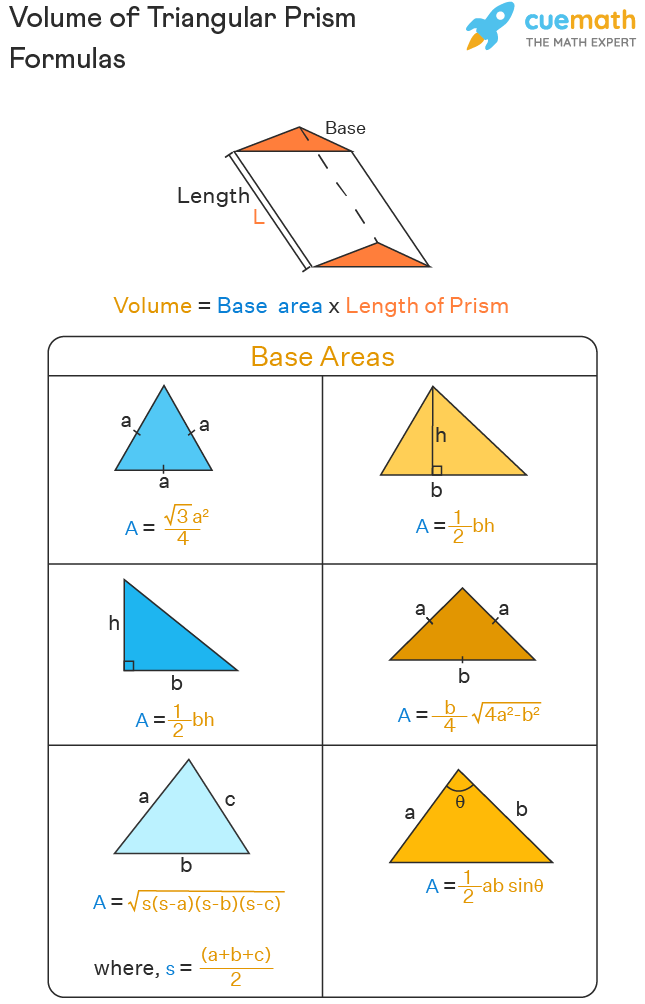
The **volume of a triangular prism** is a fundamental concept in solid geometry that involves understanding the relationship between the base area and height of the prism. The **formula for volume** can be succinctly expressed as the product of the area of the triangular base and the prism’s height. This concept is not only crucial for academic purposes but also has various practical applications in everyday life, construction, and engineering. For those interested in uncovering the intricacies of volume calculation, exploring the geometry of triangular prisms opens the door to a variety of mathematical principles and real-world applications.
Formula for Volume of a Triangular Prism
To derive the volume of a triangular prism, one must first determine the **base area** of the triangular face. This can be calculated using the **triangle area formula**, which varies depending on the type of triangle being measured. For example, for a right triangle, the area can be determined using the formula: Area = (base x height) / 2. Once the area is calculated, the volume can then be found with the equation: Volume = Base Area x Height of Prism. This formula is crucial as it lays the foundation for more complex calculations involving **volume with triangular bases**.
Calculating Volume: A Step-by-Step Approach
When **calculating volume**, it is essential to follow specific steps to ensure accuracy. Begin by identifying the dimensions of the triangular base—this includes measuring the base and height of the triangle. Then, calculate the area of the triangular base, followed by measuring the height of the prism itself. Finally, apply the \(Volume = Base Area \times Height of Prism\) formula. This step-by-step method not only aids in achieving precise **volume calculations** but also reinforces a student’s **conceptual understanding** of geometric principles.
Practical Applications of Volume Calculation
Calculating the **volume of 3D shapes**, particularly in architecture and engineering, significantly impacts design processes and structural stability. For instance, when constructing a water tank in the shape of a triangular prism, understanding the volume is crucial for determining how much water can be stored. This practical approach demonstrates the **real-life applications of geometry**, where having a solid grasp on measurements and **volume estimation techniques** can lead to effective designs and constructions. Additionally, volume calculations are also essential in industries such as manufacturing and landscaping, where space and resource optimization are paramount.
Components in Volume Calculation
To effectively calculate the **volume of a triangular prism**, several components play a critical role in the process. Understanding the triangular base’s properties is essential, whether it’s isosceles or equilateral, as this directly influences area calculation and, subsequently, the total volume.
Height Measurement Techniques
Accurately determining the **height measurement** of the prism can often be tricky, particularly for students learning the concepts. To measure the height correctly, it’s vital to ensure that it is perpendicular to the base. Various height measurement techniques, such as the use of a ruler aligned directly with the base, can be applied. In flat triangular prisms, this measurement is straightforward, while starting students might require additional illustrations or **visual mathematics** to effectively understand these concepts.
Understanding Triangular Base Areas
Each type of **triangular base** has unique properties influencing its area. For regular triangular prisms (like equilateral triangles), specialized formulas are utilized that account for the characteristics of the specific triangle. For instance, in **triangular prism examples**, recognizing whether you’re dealing with scalene, isosceles, or equilateral triangles is fundamental for accurately applying the triangle area formula, thereby influencing the overall prism volume. This sort of differentiation enriches a student’s ability to comprehend geometry’s rich tapestry.
Exploring Types of Prisms and Volume Calculations
To deepen one’s understanding of volume calculations, it’s also beneficial to explore other related prisms. For example, comparing the **volume of non-regular prism volumes** alongside triangular prisms provides insight into the characteristics that influence measurement and calculation techniques. By assessing how visiting dimensions impact calculated volumes, individuals can cultivate a more comprehensive comprehension of solid figures and their properties. Through visual aids and practical demonstrations, students can see the disruption in volume estimates and gain a better grasp of the real implications surrounding their calculations.
Volume of Composite Shapes and Conversion Techniques
Volume measurement techniques often extend to composite shapes, which incorporate various geometric figures. This section will look into how techniques apply to these more complex structures.
Calculating Volume of Composite Shapes
When confronted with **composite shapes**, understanding how to calculate volume becomes increasingly complex yet rewarding. By breaking down the composite shapes into their simpler components (such as rectangular prisms and triangular prisms), one can bolster their volume calculation skills effectively. Adding the volumes of the decomposed elements aligns with the volume of composite shapes concept where the sum of the parts directly relates to the whole—a crucial concept in integrating volume computations into broader geometric contexts.
Volume Unit Conversions
Once volume has been calculated, the next consideration is the use of appropriate units. Understanding **volume unit conversions** is vital, especially when applying volume in different fields. For instance, cubic meters may need to be converted to liters for liquid measurement. Keeping a conversion chart handy allows for smoother calculations and broader comprehension across measurements. This aspect of mathematical modeling is widely sought after in fields leveraging practical geometry applications.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the relationship between base area and height of a triangular prism leads to effectively finding **volume calculation**.
- Mastery of the **triangle area formula** is crucial for accurate volume measurement.
- Practical applications of volume calculations demonstrate the relevance of geometry in real-life scenarios.
- Bringing in concepts like **volume of composite shapes** facilitates a more robust understanding of geometric properties.
- Unit conversion understanding is key to effectively applying calculated volumes across different contexts.
FAQ
1. What is the general formula for finding the volume of a triangular prism?
The general formula for calculating the **volume of a triangular prism** is expressed as: Volume = Base Area × Height. This requires the area of the triangular base to be determined first using methods suitable for the triangle type, and then multiply that area by the prism’s height. This formula forms a fundamental principle in the geometry of triangular prisms.
2. How do you find the area of a triangular base?
To find the area of a triangular base, use the formula: Area = (Base × Height) / 2. Knowing the height (altitude of the triangle) is crucial for accurate area calculation. Depending on the triangle type, additional formulas such as Heron’s formula can also be employed. Approaching the area from varied angles enhances the **spatial reasoning** required for solid geometry.
3. What types of prisms exist, and how do their volume calculations differ?
Prisms can be categorized primarily as **regular prisms** and **non-regular prisms**. Their volume calculations differ based on base shape. Regular prisms have uniform faces and standard dimensions. In contrast, non-regular prisms require more intricate calculations due to varying base properties. Understanding these distinctions is essential in mastering geometry.
4. Can volume of triangular prisms be relevant in real-life applications?
Absolutely! Understanding the **geometry of triangular prisms** is highly relevant in practical fields, such as architecture, engineering, and design. For example, determining the volume of a triangular prism is vital for designing water reservoirs, where precise volume estimates directly influence functionality and safety. Such practical applications highlight the **importance of geometry** in everyday tasks.
5. How can technology aid in volume calculations for complex shapes?
Technology, particularly in **3D modeling**, enhances volume calculations through software specifically designed for geometry. These applications often allow users to visualize shapes, calculate properties swiftly, and manipulate parameters effectively. Thus, integrating technology into geometric calculations supports better understanding and accuracy in measurements, laying a solid foundation for advanced spatial reasoning.
“`