Effective Ways to Simplify Square Roots for Better Understanding in 2025
Simplifying Square Roots: The Basics
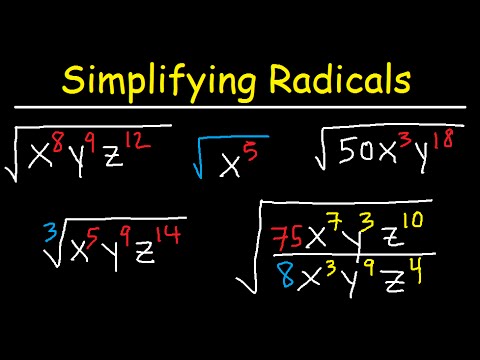
When it comes to **simplifying square roots**, the fundamental goal is to express a square root in its simplest form. Understanding **square root properties** is crucial, as it enables students and individuals alike to tackle a variety of mathematical problems with ease. A key point is to recognize **perfect squares**, which are numbers that have whole number roots (e.g., 1, 4, 9, 16, etc.). Utilizing the **square root rules**, we can simplify roots that stem from these perfect squares effectively. For instance, the square root of 36 is a perfect square and can be simplified to 6. By grasping these basics, a solid foundation is laid for exploring more complicated calculations involving square roots.
Understanding Perfect Squares and Their Applications
Perfect squares form the backbone of many simplification processes. By identifying common square roots, we can quickly extract useful information when given more complex square roots. For example, simplifying √(75) can be achieved by recognizing that it can be broken down into √(25 * 3), which simplifies to 5√3. This method not only streamlines the process but also enhances understanding of **fractional square roots** in conjunction with numerical approaches such as factorization. In practice, introducing visuals such as **radical expressions** can significantly enhance one’s ability to grasp these concepts quickly.
Mastering Square Root Multiplication and Division
When approaching **square root multiplication**, it’s vital to remember that the square root of a product equals the product of their square roots (that is, √(a * b) = √a * √b). This rule makes it simpler to manage larger square roots. For example, √(50 * 2) can be broken down immediately to √100, which simplifies straightforwardly to 10. Likewise, in **square root division**, applying the rule √(a/b) = √a / √b gives us a streamlined approach to handle division of square roots. With continued practice through **square root exercises** focused on applications in both multiplication and division, these skills will develop naturally.
Radical Expressions and Simplification Strategies
Simplifying **radical expressions** involves various techniques that revolve around recognizing and implementing the previously discussed properties and rules. This section delves deeper into advanced methods such as **rationalizing denominators**, which frequently comes into play when working with fractions that contain square roots. In addition to this, mastering the **arithmetic with square roots** is crucial as it can apply in numerous creative ways in Algebra.
Rationalizing Denominators: A Necessary Skill
Rationalizing the denominator involves eliminating square roots from the denominator of any fraction. For instance, if you encounter 1/√2, it can be rationalized by multiplying both the numerator and denominator by **√2**. Thus, it transforms into √2 / 2. This technique is beneficial in maintaining the standard form of rational numbers and aids in deeper **algebraic simplification** for students learning to manipulate radicals effectively.
Applying Square Root Formulas in Practical Applications
Square root formulas play a significant role in various practical contexts ranging from geometry to statistics. Understanding how to manipulate these roots allows individuals to solve real-world problems efficiently. For example, if tasked with finding the distance between two points on a plane using the distance formula, you will be applying the properties of square roots directly. Emphasizing real-world problems can motivate learners to appreciate the significance of **square roots in algebra** and beyond, revealing how frequent their applications are in day-to-day computations.
Engaging with Square Roots: Techniques and Strategies
With foundational skills established, the focus shifts toward engaging methodologies in teaching square roots. Whether through interactive lessons or visual aids, the integration of diverse formats helps relay complex ideas simply. **Understanding square roots linguistically** can be vital, especially when it comes to assisting younger students or individuals new to mathematics.
Visualization and Historical Methods for Square Root Simplification
Visual learning aids, such as diagrams or charts illustrating common square roots, support comprehension and retention. Additionally, exploring the **historical evolution of square roots** might unveil various methods utilized throughout maths. These themes can provide insight not just into how square roots can be simplified but also into the reasoning behind the techniques. This deeper engagement may come in handy particularly during **teaching square roots** where traditional memorization fails.
Interactive Square Root Lessons and Games
Adopting playful learning experiences such as **square root games** or simulations can enhance understanding while making the learning process enjoyable. Systems can be set up for students to practice calculating square roots quickly while scaffolding knowledge through competitive or collaborative efforts. This excitement surrounding arithmetic with square roots is likely to encourage mastery and confidence in any mathematical environment.
Mastering Square Roots in 2025 and Beyond
The ongoing endeavor to master **simplifying square roots** will benefit significantly from combining traditional methods with contemporary strategies. These approaches will prove invaluable as mathematics continues to progress and become increasingly relevant to various fields. Enabling students to visualize and articulate these concepts promotes a profound understanding that extends past immediate calculations into deeper mathematical thought.
Applying Technology to Square Root Practice
In today’s digital age, leveraging technology for square root practice can enhance learning significantly. Numerous online platforms offer exercises and explanatory tools that can aid in understanding simplifying square roots. Using educational software or applications designed for **square root calculations** provides immediate feedback and allows learners to engage with square roots dynamically.
Building a Strong Framework through Consistent Practice
Ultimately, constructing a reliable foundation in understanding square roots starts with regular engagement and practice. As students are frequently presented with **square root examples**, they’ll grow comfortable with simplification protocols, making them more adept in contexts requiring **numerical approaches to square roots**. Regularly revisiting these simplified forms within different numerical scenarios will reinforce their learning indefinitely.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding basic **square root properties** is crucial for simplification.
- Recognize **perfect squares** to simplify square roots efficiently.
- Essential arithmetic techniques include **square root multiplication** and **division**.
- Engaging methodologies in teaching foster deeper understanding and retention of concepts.
- Technology and interactive lessons can enhance practice and mastery of square roots.
FAQ
1. What are some effective simplifying techniques for square roots?
Effective simplifying techniques for square roots include identifying and factoring out perfect squares. This includes recognizing common square roots such as \( \sqrt{25} = 5\) and expressing roots in combinations that facilitate simplification. For example, breaking \( \sqrt{72} \) into \( \sqrt{36 \cdot 2} \) results in \( 6\sqrt{2} \). Mastery of perfect square factoring is fundamental.
2. How does one rationalize denominators containing square roots?
To rationalize a denominator with a square root, you multiply both the numerator and denominator by the square root present in the denominator. For example, for \( \frac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \), multiply by \( \frac{\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}} \) resulting in \( \frac{\sqrt{3}}{3} \). This technique eliminates the square root from the denominator and results in a more manageable fraction.
3. Are there any rules governing square root addition and subtraction?
The rules for square root addition and subtraction state that you can only directly add or subtract square roots that are the same, known as like radicals. For example, \( 2\sqrt{5} + 3\sqrt{5} = 5\sqrt{5} \). However, \( \sqrt{8} + \sqrt{9} \) cannot be simplified directly; instead, simplifications would be conducted separately, resulting in like terms afterward.
4. How can visualization help in understanding square roots?
Visualization aids comprehension by allowing learners to see the relationships between numbers and their square roots. Using charts, number lines, or geometric interpretations can illustrate how certain roots correspond graphically to numbers, making concept assimilation more seamless for students learning about square roots.
5. What role does practice play in mastering square roots in algebra?
Consistent practice is critical in mastering square roots. By regularly engaging with different exercises that pertain to **square root calculations**, learners can strengthen their abilities and retain knowledge more effectively. Repetition cements understanding and confidence in applying **square root properties** to various algebraic contexts.
6. What are common applications of square roots in real life?
Square roots feature prominently in numerous real-life applications including engineering, physics, and computer science. For instance, calculating distances involves square roots, such as when employing the Pythagorean theorem to determine the length of a side in a right triangle. They are also critical in financial scenarios involving quadratic formulas and statistics.
7. Can you explain the concept of irrational square roots?
Irrational square roots emerge when a number does not have an exact square root that can be expressed as a simple fraction or whole number. Examples include \( \sqrt{2} \) and \( \sqrt{3} \); these cannot be simplified into a finite decimal or proper fraction. Recognizing irrational numbers is a key point in advanced algebraic contexts where square roots arise.