How to Properly Use a Protractor: Essential Tips for Accurate Measurements in 2025
Protractors are fundamental **angle measurement tools** widely used in mathematics and construction. Understanding **how to use a protractor** effectively can greatly enhance accuracy in measuring angles and drawing geometric shapes. In this guide, we will explore the proper techniques and tips for both beginners and advanced users, ensuring precise results in your measurements. We will start by discussing the **various types of protractors**, then move on to practical applications, common mistakes to avoid, and conclude with FAQs to reinforce your learning.
Understanding Protractor Types
When selecting a protractor, it’s important to recognize that there are different **types of protractors** designed for specific functions. The most common types are the circular protractor, which provides a 360-degree measurement, and the semi-circular or half protractor, which measures angles up to 180 degrees. Each type serves distinct purposes in various fields like educational math tools, engineering, and architecture.
Common Protractor Models
Familiarizing yourself with the **most common protractor models** can aid in selecting the right one for your needs. For educational use, plastic protractors are popular due to their durability and flexibility for hands-on activities. Digital protractors are emerging as a new tool in geometry, offering users instant measurements displayed on a digital screen, aligning perfectly with modern technology in measuring angles.
Choosing the Right Protractor for Your Needs
When it comes to serious construction or architecture work, choosing a specialized **protractor for precise angles** may be necessary. Professional-grade protractors often come with additional geared adjustments that allow for better precision when marking angles. Therefore, evaluate what you will primarily use the protractor for to ensure you make the best choice.
Basic Protractor Usage
Learning the **basic protractor usage** is essential for accurate **angle measurement**. By employing step-by-step techniques, one can effectively measure both acute and obtuse angles. Proper orientation and alignment are crucial in ensuring your measurements yield reliable results.
Step-by-Step Protractor Guide
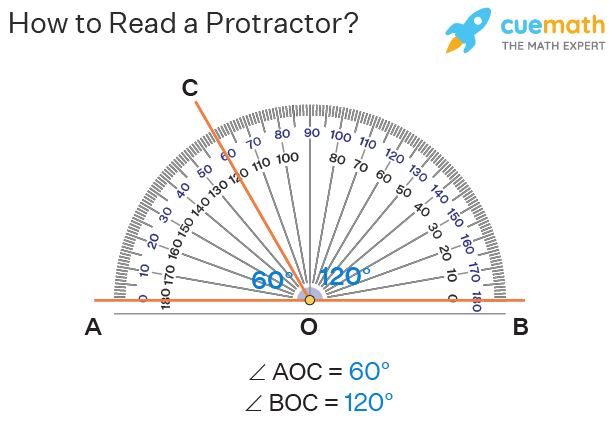
To measure an angle with a protractor, follow this **step-by-step protractor guide**: first, place the midpoint of the protractor’s straight edge on the vertex of the angle. Align one ray of the angle with the 0-degree line of the protractor. Finally, follow the curve of the protractor to determine where the other ray intersects the markings, which will give you the angle’s degree measurement. This straightforward process emphasizes the significance of **proper protractor alignment** and understanding the **protractor markings**.
Practical Uses of a Protractor in Education
Integrating a protractor into everyday math lessons can enhance students’ **mathematical literacy** and understanding of angle relationships. For instance, teachers can use it in classroom projects that involve measuring angles in geometric shapes and creating angle bisectors. Incorporating interactive resources and geometry worksheets into lessons can make measuring angles engaging and memorable for students.
Measuring Angles Step by Step
Once you grasp the basics of using a protractor, you can move towards advanced techniques in **measuring angles with a protractor**. Here, we take a more detailed view of what each type of angle measurement entails, alongside methods to visualize these dimensions accurately.
Measuring Acute and Obtuse Angles
Acute angles are those measuring less than 90 degrees, while obtuse angles measure more than 90 degrees and less than 180 degrees. When **measuring acute angles**, ensure that the protractor vertex is positioned correctly, as this will influence the accuracy of your results. For obtuse angles, utilize the similar alignment method, and remember to visualize measurement results to reinforce comprehension of the angle’s dimension.
Common Mistakes with Protractors
New users often make common mistakes, such as misplacing the protractor or reading it backward. It’s crucial to maintain focus on **proper protractor orientation** throughout the measurement process to avoid inaccuracies. Additionally, take the time to familiarize yourself with **understanding protractor markings**, as being attentive to detail can significantly impact the quality of your work.
Advanced Protractor Techniques
As users advance in their skills, they may want to explore **advanced protractor usage**, diving deeper into construction-related activities. This includes techniques for accurate angle drawing and understanding the protractor’s role in professional practices. Gaining quantitative insights into angles will open additional opportunities in fields such as physics and architecture.
Using a Protractor for Construction
In construction, precision is vital, and knowing **how to measure angles** accurately is paramount. When using a protractor for construction projects, adjustments and correct measurements will be necessary, ensuring that structures being built are accurate. Implementing high-quality tools and adhering to professional standards will ensure the success of the project.
Practical Projects with a Protractor
DIY enthusiasts can explore various **DIY protractor projects**, like creating custom geometric patterns or constructing models requiring specific angle measurements. Such practical applications promote a hands-on understanding of measuring angles, enhancing spatial awareness and mathematical fluency.
Key Takeaways
- Different protractor types suit various applications, from educational to construction use.
- Accurate alignment and understanding markings are essential for effective angle measurements.
- Recognizing and managing common mistakes can enhance measurement skills.
- Advanced techniques broaden the functional uses of protractors beyond basic applications.
FAQ
1. What are the basic functions of a protractor?
A protractor is primarily used for measuring angles in degrees. They can also be employed in drawing specific angles, making it an essential tool in geometry and construction projects. Familiarizing oneself with **understanding angle measurements** can enhance one’s overall mathematical skills.
2. How can I avoid common mistakes while using a protractor?
To avoid common mistakes like misalignment and incorrect readings, begin by ensuring your protractor’s center is positioned at the angle’s vertex. Focus carefully on which scale to read (inside or outside) and ensure that your line of sight is aligned with the protractor marks, effectively preventing inaccuracies.
3. What are some advanced uses of a protractor in construction?
In construction, a protractor can be used for precise angle measuring, making models for building designs, and crafting plans that require specific angles. Understanding **protractor techniques** can assist architects and engineers in creating accurate schematic designs that meet professional standards.
4. How do different protractor types affect measurement accuracy?
Different protractor types can significantly influence measurement accuracy. For example, digital protractors and laser-based models offer more precise functionality than traditional plastic models. Understanding the attributes of these **measuring tools** allows for smarter choices in both educational and construction settings.
5. What role do educational resources play in learning how to use a protractor?
Educational resources such as geometry apps, interactive tools, and worksheets enhance the learning experience about **using a protractor**. These resources offer varying methods for practicing measurement techniques and reinforce skills through engaging activities within math education.
For further resources and visual aids, feel free to check the diagrams and images associated with protractor usage: