Effective Ways to Master Synthetic Division in 2025
Understanding Synthetic Division
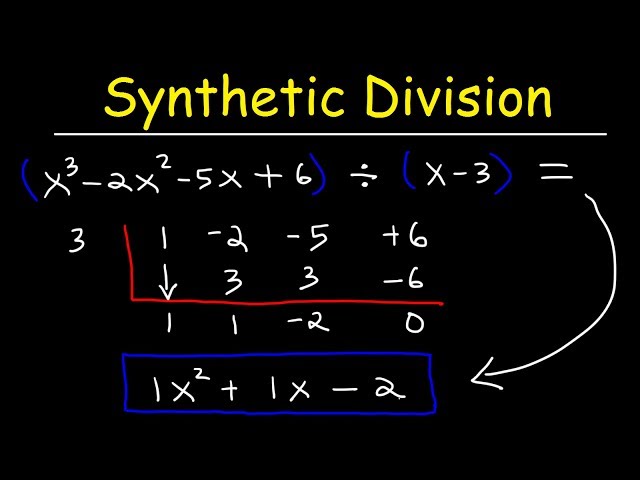
Synthetic division is a streamlined method for performing **dividing polynomials**, specifically when dealing with linear factors. Unlike **polynomial long division**, synthetic division simplifies the process by focusing on the coefficients of the polynomial, allowing for quicker calculation. This technique is particularly useful when solving polynomial equations or evaluating polynomials at specific values. With the **synthetic division algorithm**, you can derive the **quotient** and **remainder** when dividing by a binomial of the form (x – c). Understanding synthetic division can significantly enhance your efficiency in algebra, especially in tackling complex polynomial problems.
What are Coefficients and Their Role?
In synthetic division, the coefficients of the polynomial play a crucial role. They are the numerical factors that precede each term of the polynomial. For example, in the polynomial expression 2x³ + 3x² – 5x + 1, the coefficients are 2, 3, -5, and 1. When performing synthetic division, you only need to write down these coefficients, which streamlines the entire process. This method not only simplifies the calculations but also aids in **finding the roots of polynomial** equations easily. Understanding how to manipulate these coefficients can lead to a deeper comprehension of polynomial functions and their **behaviors**.
Synthetic Division Steps: Simplifying the Process
To effectively execute synthetic division, follow these simplified steps:
1. Write down the coefficients of the polynomial.
2. Place the **divisor** (in the format x-c) on the left side of your setup and the coefficients on the right.
3. Bring down the leading coefficient.
4. Multiply this leading coefficient by c and write the result beneath the next coefficient.
5. Add the columns together, repeating this multiplication and addition until you have processed all coefficients.
6. The final row will give you the **quotient** coefficients, and the last number will represent the **remainder**. By utilizing these synthetic division steps, you can efficiently manage the division of higher degree polynomials.
Applications of Synthetic Division
Synthetic division is not only a mathematical technique but also a problem-solving strategy applicable in various fields. It is particularly useful in calculus and numerical methods for simplifying the analysis of polynomial functions. You can leverage synthetic division when evaluating limits or roots within polynomial approximations. Furthermore, understanding how to apply these methods can enhance your ability to process complex algebraic functions effectively.
Linking Synthetic Division to the Remainder Theorem
The **remainder theorem** states that for any polynomial p(x), if p(x) is divided by (x – c), the remainder is equal to p(c). Utilizing synthetic division, this theorem becomes a practical tool for evaluating **polynomial expressions** efficiently. Simply substitute c into the synthetic division, and the last value (the remainder) gives you the value of the polynomial at that point. This connection simplifies the process of finding polynomial values, especially when checking solutions or evaluating expressions without having to substitute manually each time.
Case Study: Solving a Problem with Synthetic Division
Let’s apply synthetic division to a concrete example. Suppose you want to divide the polynomial 3x³ – 5x² + 4x – 2 by x – 1. Using the coefficients 3, -5, 4, and -2, you would set up as follows:
1. Write down the coefficients: 3, -5, 4, -2.
2. Place 1 (from x-1) on the left.
3. Perform the synthetic division, yielding the coefficients of the quotient polynomial: 3x² – 2x + 2, with a remainder of 0. This means (x – 1) is a factor of the polynomial. Through this simplified technique, complex calculations become manageable and clear.
Mastering Polynomial Functions via Synthetic Division
Improving your ability to handle polynomial functions through synthetic division will greatly enhance both your academic performance and practical application of algebra. As you practice **dividing polynomials**, focus on recognizing patterns and understanding the underlying theories. Mastery of these techniques brings considerable ease not only in academic studies but also in fields requiring advanced mathematical comprehension.
Applying Numerical Methods with Synthetic Division
Navigating complex numerical computations becomes more accessible through synthetic division. This technique helps in testing numerical solutions for equations and for assessing the behavior of polynomial functions across real numbers. If you are solving quadratic equations or higher degree polynomials, adopting synthetic division can streamline those processes, allowing quicker and more accurate evaluations. As the complexity of polynomials increases, so does the necessity for efficient computational methods, and synthetic division fits perfectly into that niche.
Using Graphical Interpretation for Understanding Division
Graphically interpreting synthetic division can clarify concepts related to polynomial identities. When evaluating polynomials, visualize the actions of division as transformations on the polynomial graph. The roots found through synthetic division correlate directly with the x-intercepts of the polynomial’s graphical representation. Tools like graphing calculators or software can assist in visualizing these functions. By connecting graphical interpretation with synthetic division, you’ll be better equipped to understand polynomial behavior.
Key Takeaways
- Synthetic division simplifies obtaining the **quotient** and **remainder** from polynomial division.
- Understanding the role of **coefficients** is crucial in implementing synthetic division effectively.
- Synthetic division is particularly useful when linked with the **remainder theorem** for evaluating polynomial expressions quickly.
- Graphical interpretations can enhance understanding and facilitate a deeper grasp of polynomial functions.
FAQ
1. What is synthetic division in simple terms?
Synthetic division is a shortcut method for dividing polynomials when the divisor is a linear binomial of the form (x – c). It allows for quick calculations using the polynomial’s coefficients, omitting more tedious long division processes.
2. When should I use synthetic division instead of polynomial long division?
Synthetic division is preferable when the divisor is a simple linear polynomial, such as (x – c). It is faster and less error-prone, especially for higher degree polynomials, making it a highly efficient tool for algebraic computations.
3. Can synthetic division be used for any degree polynomial?
Yes, synthetic division can be used for polynomials of any degree, but it is primarily effective for linear factors. For other divisors, polynomial long division may be necessary. This versatility allows synthetic division to be integrated into various mathematical tasks.
4. What are the limitations of synthetic division?
While synthetic division is efficient, it is limited to linear divisors. Additionally, if the polynomial is not in descending order of degree, you may encounter complications. Understanding these boundaries is crucial for correctly applying the division process.
5. How can I practice synthetic division effectively?
To practice synthetic division, consider working on various polynomial problems, assessing both their **roots** and resulting **quotients**. Online resources, algebra tutorials, and dedicated homework exercises can enhance your skills. Visualization through graphing calculators can also reinforce conceptual understanding.