“`html
How to Become a Dermatologist: A Comprehensive Guide for 2025
Becoming a dermatologist is an exciting and rewarding career path dedicated to skincare, diagnosis, and treatment of skin conditions. With advancements in dermatology, including innovative procedures and burgeoning research opportunities, aspiring dermatologists must understand the essential steps required to enter this promising field. In this guide, we’ll explore how to become a dermatologist, diving deep into the necessary education, residency requirements, and future trends in dermatology.
Understanding the Dermatologist Career Path
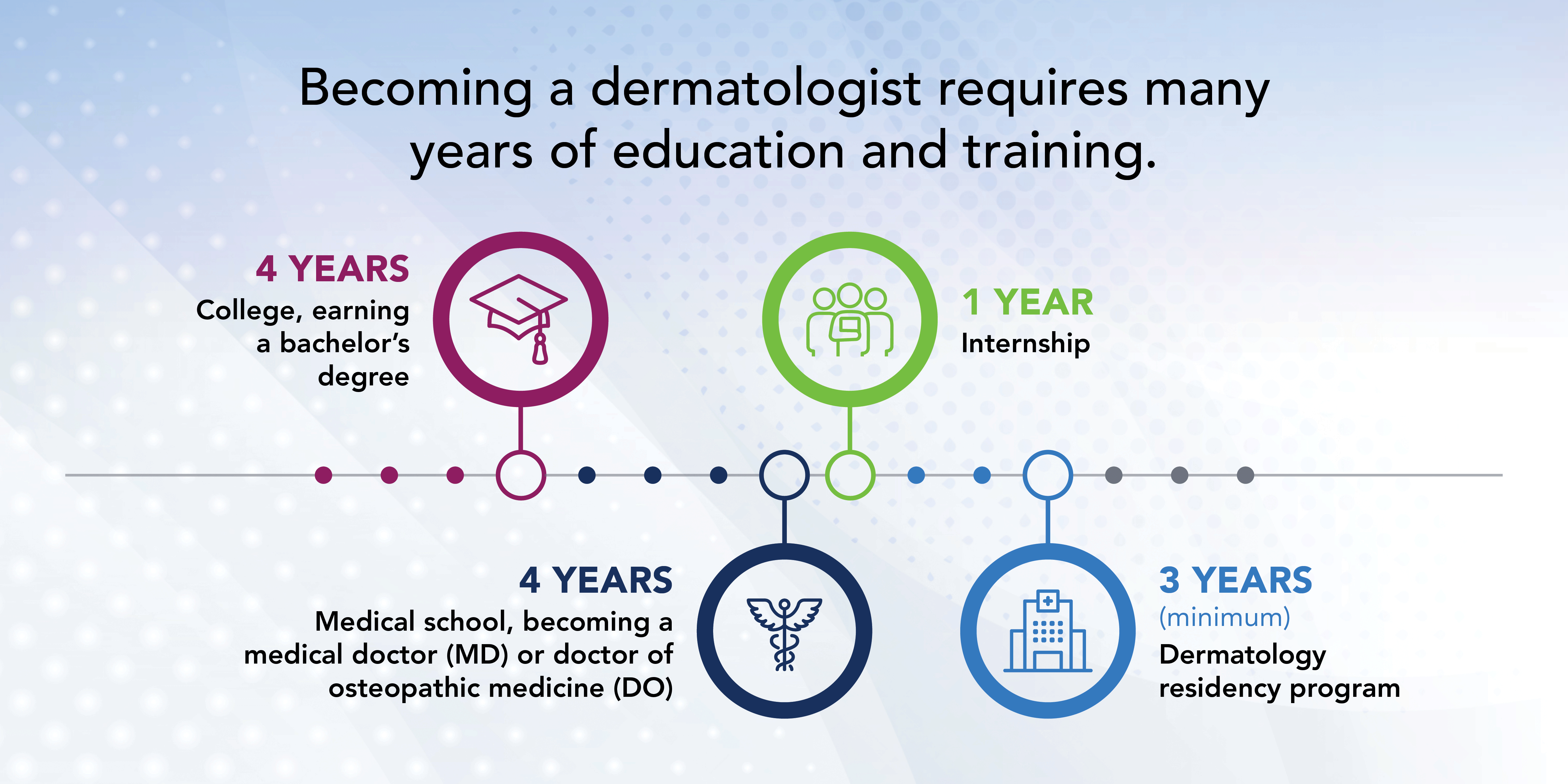
The journey to become a dermatologist begins with a foundational understanding of the dermatologist career path. This entails completing undergraduate education, medical school, and pursuing a residency specifically tailored to dermatology. Each stage plays a vital role in equipping students with the clinical experience and specialized knowledge they need to excel in their careers. Aspiring dermatologists must also engage in extracurricular activities such as internships, outreach programs in dermatology, and networking opportunities to broaden their understanding and strengthen their professional relationships within the field.
Medical School for Dermatologists
The first major step in the dermatologist career path is enrolling in a reputable medical school for dermatologists. Medical school typically takes four years and includes coursework in various medical disciplines including anatomy, pharmacology, and pathology. Students should strategically select electives related to dermatology to enhance their curriculum. Additionally, seeking opportunities for summer internships in dermatology clinics during medical school can significantly boost one’s knowledge and improve skills essential for future residency programs. It’s also important to prepare for the dermatology certification exam by focusing studies on key areas pertaining to dermatological diagnoses and treatments.
Residency Application Process
The application process for dermatology residency is highly competitive, requiring candidates to demonstrate a strong academic record, relevant experience and excellent referral letters. Typically, students must have completed a year-long internship in an accredited medical residency program before applying specifically to dermatology residencies. In addition to passing the United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE), gaining research experience, and participating in leadership roles can significantly bolster an application. Individuals should also actively seek advice and mentorship from current residents or practicing dermatologists, as this can provide useful insights into the residency experience.
Residency in Dermatology
After successfully completing the residency application process, candidates must undertake a residency in dermatology that generally lasts three years. During this time, residents receive extensive training in managing a variety of skin conditions through clinical experience in dermatology. This includes rotations through various dermatological subspecialties such as pediatric dermatology and cosmetic dermatology, providing a comprehensive understanding of different areas within the field. Residents hone their skills in dermatological procedures, conduct hands-on patient care, and often contribute to ongoing dermatology research opportunities.
Essential Skills for Dermatologists
Having a deep understanding of the essential skills for dermatologists is crucial for success in this profession. Apart from a solid medical foundation, dermatologists must possess excellent communication skills to effectively interact with patients and colleagues. Empathic communication plays a major role, particularly in discussing sensitive skin conditions. Furthermore, dermatologists need technical skills to perform various dermatological procedures and understand the usage of the latest technology and tools in dermatology.
Understanding Dermatological Tools and Procedures
Knowledge of dermatological procedures is integral for dermatologists. Familiarity with surgical and non-invasive treatment options allows dermatologists to address patients’ diverse skin conditions. They must be well-versed in procedures such as biopsies, laser treatments, and skin cancer treatments. Additionally, understanding how to use advanced diagnostic tools, such as dermoscopy, enhances accuracy in skin condition diagnosis. Participating in dermatology workshops can also be beneficial for staying updated on the latest advancements and techniques.
Continuing Education for Dermatologists
Given the rapid evolution within the field, continuing education for dermatologists is essential. Dermatologists are often required to pursue ongoing training to maintain their board certification, attending medical conferences, or enrolling in online dermatology courses. These educational activities expose dermatologists to the latest research, technology advancements, new treatment options, and current guidelines for patient care in dermatology. Establishing a plan for lifelong learning ensures practitioners remain knowledgeable and competent throughout their careers.
Building Patient Rapport and Care
Pairing clinical expertise with empathetic patient care in dermatology can significantly improve patient satisfaction and their overall treatment experience. Successful dermatologists cultivate strong relationships with their patients through effective listening, understanding their concerns, and tailoring treatment plans accordingly. Improving patient access to dermatology services is another area where dermatologists can excel, particularly through teledermatology and telemedicine practices, which are rapidly gaining popularity.
The Role of Technology in Dermatology
As the healthcare field increasingly embraces technology, understanding its impact is vital for dermatologists. The role of technology in dermatology encompasses various tools, including telemedicine platforms, electronic Health Record (EHR) systems, and imaging technologies. Implementing innovative approaches opens new avenues for managing patient care and fosters better delivery of dermatological services. Mastering these technologies not only streamlines workflows but also enhances patient outcomes significantly.
Trends in Dermatology
Keeping abreast of trends in dermatology is critical for both aspiring and established dermatologists. As dermatology evolves, emerging specialties such as integrative dermatology and pediatric dermatology are becoming paramount due to their growing importance in patient care. Additionally, wellness trends are making significant impacts; for instance, skincare advice overlaps with dermatological expertise. Dermatologists should advocate for public health initiatives focusing on the importance of skin health, including outreach programs to educate communities on skin disease prevention and care.
Networking and Professional Organizations
Engaging with various dermatology professional organizations and participating in conferences provides tremendous networking opportunities for dermatologists. Joining associations such as the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) or local dermatology groups can offer resources for education, mentorship, and possible job openings. These connections enhance reputation and collaboration among professionals, which can ultimately lead to improved patient therapies and advanced research initiatives in dermatology.
Key Takeaways
- Pursuing a dermatologist career requires extensive education and training, starting from undergraduate studies through medical school and finishing with residency.
- Essential skills include advanced technical capabilities in dermatological procedures, effective communication, and empathy in patient care.
- Ongoing education, including attending conferences and joining professional organizations, is necessary to stay current in this ever-evolving field.
- Understanding the latest technology trends in dermatology can significantly enhance patient outcomes and service delivery.
- Networking plays a critical role in professional development within dermatology, often leading to collaboration and advancement opportunities.
FAQ
1. What dermatology education requirements should I be aware of?
The essential dermatology education requirements include completing a bachelor’s degree, followed by a medical degree (MD or DO). This is succeeded by three years of residency training focused on dermatology, where practical skills and knowledge specific to the field are gained.
2. What kind of work environment can dermatologists expect?
Dermatologists typically work in a variety of settings, such as private dermatology clinics, hospitals, and academic institutions. Their work environment can range from clinical consultations to performing outpatient procedures, indicating a mix of patient-facing duties and technical work.
3. Why are continuing education courses important for dermatologists?
Continuing education courses are crucial as they help dermatologists stay abreast of the latest advancements in skincare technology, treatment protocols, and best practices. This mandatory learning helps in maintaining their board certification and delivering the most effective patient care.
4. What is the typical job outlook for dermatologists?
The job outlook for dermatologists remains positive, with increasing awareness of skin health continuing to drive demand for dermatological services. The field has seen growth due to rising incidences of skin conditions and an increase in cosmetic procedures.
5. How can I improve my chances of being accepted into a dermatology residency?
To improve your chances of acceptance into a dermatology residency, focus on achieving high academic performance, gaining relevant clinical experiences like internships, obtaining strong letters of recommendation, and maintaining an active involvement in dermatological research and professionalism throughout your medical school journey.
6. Are there specialized areas within dermatology?
Yes, dermatology encompasses various specialized fields, including pediatric dermatology, cosmetic dermatology, and dermatopathology. Each specialization allows dermatologists to focus on specific patient needs and treatment types, thus enhancing their impact in dermatologic care.
7. What advice do dermatologists have around skincare practices?
Dermatologists often emphasize the importance of sun protection, using broad-spectrum sunscreen daily, understanding different skin types, and addressing specific conditions like acne or eczema effectively. Maintaining a consistent skincare routine that includes hydration and using dermatologist-recommended products is vital for overall skin health.


“`