Smart Ways to Find the Interquartile Range in 2025
Understanding the Interquartile Range
The **interquartile range** (IQR) is a vital statistical measure that represents the middle 50% of a data set. It is a significant tool in **statistics** for understanding data spread and detecting outliers. The IQR is calculated by finding the difference between the upper quartile (Q3) and the lower quartile (Q1). This measure not only provides concise information about data variability but also serves as a robust analysis technique in various fields like finance and research. Understanding the IQR can assist in making informed decisions based on data, making it crucial for statistical reporting and analysis.
Definition of Interquartile Range
The **definition of interquartile range** is straightforward: it quantifies the spread of the central half of the data points in a dataset. The formula used for calculating the interquartile range is IQR = Q3 – Q1, where Q3 is the upper quartile, and Q1 is the lower quartile. This statistical measure is robust, which means it is less affected by outliers compared to the total range of the dataset. For example, if your data set consists of 10 numbers, obtaining the IQR gives insight into the variability and concentration of the middle values, thus elucidating trends that could otherwise be obscured by extreme values.
Importance of Interquartile Range
The **importance of interquartile range** in data analysis cannot be overstated. It helps illuminate the degree of dispersion within a dataset, offering insights that the mean or total range might not reveal. For instance, in a business context, understanding the IQR can help identify whether most sales lie near the average or if significant outliers exist, thereby informing strategic decisions. Moreover, when visualizing data through box plots, the IQR is prominently displayed, making it easier to interpret the spread and identify potential outliers. Thus, mastering the IQR enhances skills in data interpretation, revealing patterns that are definitive in statistical research.
Steps to Find Interquartile Range
Calculating the interquartile range requires a sequence of well-defined steps. By following the proper **steps to find interquartile range**, you ensure accuracy in your statistical analysis. The core steps involve sorting the dataset and identifying the quartiles. For instance, arranging your data points in ascending order is essential because quartiles are determined based on positional data. Once sorted, you can find the median and use it to calculate both the lower and upper quartiles, ultimately leading to the IQR.
Calculating Quartiles
To accurately determine the quartiles, it is crucial to first understand how to calculate them. The quartiles split your data into four equal parts. Start by finding the median, which represents Q2 or the second quartile. The lower quartile (Q1) is then the median of the lower half of the data set (data points below Q2), while the upper quartile (Q3) is the median of the upper half. Let’s say we have the dataset: 3, 7, 8, 12, 13, 14, 18, 22, 26. The median (Q2) is 13, the lower quartile (Q1) is 8, and the upper quartile (Q3) is 18. Thus, the IQR would be 18 – 8 = 10, effectively showing the spread of the middle 50% of the data.
Steps Involved in Finding Interquartile Range
To summarize the **steps involved in finding interquartile range**: first, collect and sort the data which allows for an accurate position assessment of values. Next, identify the median to split the data into two halves. Look for Q1 and Q3 in the lower and upper halves of the data, respectively. Finally, calculate the difference between Q3 and Q1 to derive the IQR. Following these steps will enhance accuracy and provide essential insights into your data set’s dispersion.
Visualizing Interquartile Range
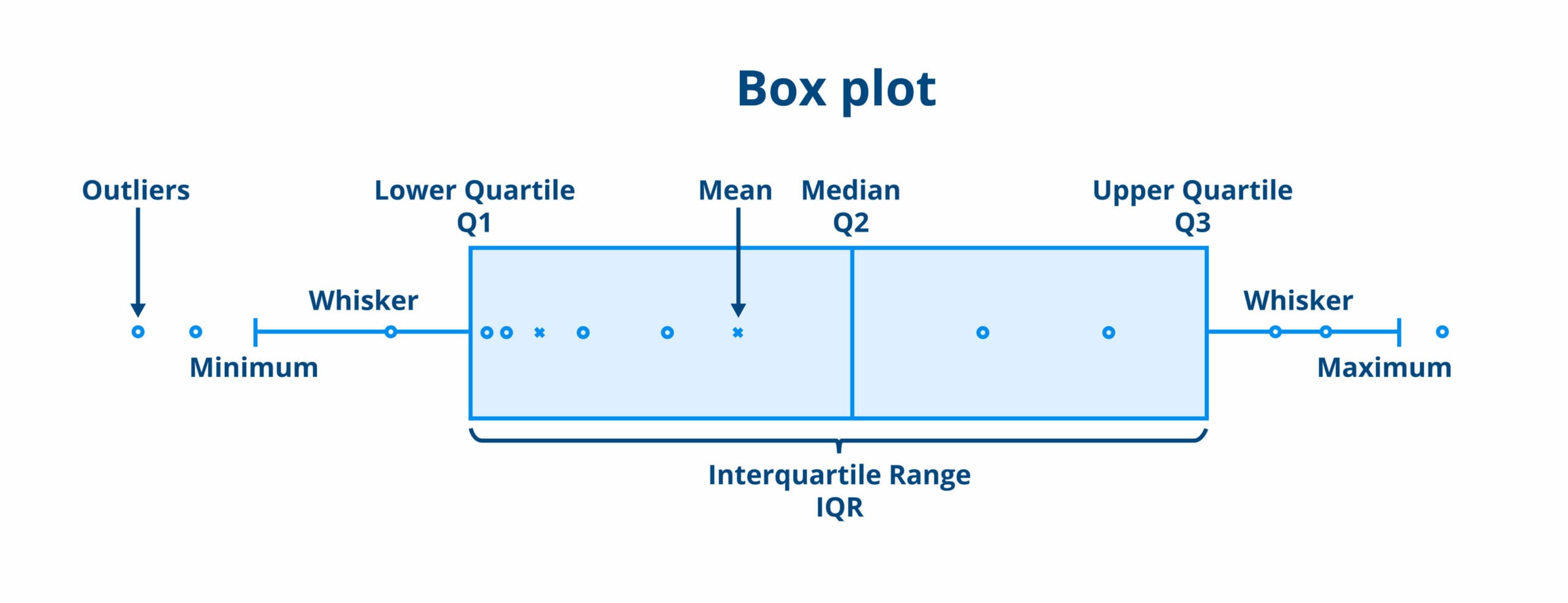
Visualization is an incredibly effective method for interpreting the **interquartile range**. One of the most common visual tools used in statistics for this purpose is the **box plot**. The box plot graphically represents the median, quartiles, and potential outliers, giving a clear layout of the data’s distribution. When you see a box plot, the length of the box shows the range of the interquartile range, while whiskers extend to the smallest and largest values, excluding outliers. This visual approach can be beneficial in presentations and during organizational analysis to underscore trends effectively.
Interquartile Range from Box Plot
Determining the interquartile range from a box plot is straightforward. In a box plot, the lower and upper edges of the box signify Q1 and Q3, respectively. Measure the box’s length to quickly grasp the IQR without additional calculations. This can also serve as a quick reference point when comparing multiple sets of data. For example, in conducting a stakeholder analysis in a business environment, presenting box plots can effectively visualize sales performance across different quarters or departments, aiding in strategic discussions.
Using Interquartile Range for Skewed Data
One of the noteworthy advantages of the interquartile range is its robustness in dealing with **skewed data**. Traditional statistical measures like the mean can be strongly influenced by outliers; however, the IQR, by design, focuses solely on the middle half of the data, circumventing extreme values. For instance, if a company’s profits show a significant spike due to an anomaly, the **interquartile range** will still accurately reflect the central tendency without being distorted, allowing for strategic business decisions based on sound analysis rather than anomalized data variations.
Practical Applications of Interquartile Range
The **applications of interquartile range** extend into multiple sectors, enhancing data analysis methodologies. In finance, the IQR is often used to identify volatility in stock prices, making it crucial for traders seeking to mitigate risk. Additionally, **interquartile range uses in research** help statisticians understand the variability in survey data or experimental outcomes, ensuring findings that are both precise and actionable. Other fields such as healthcare or education rely on the IQR for effective interpretation of data sets, ensuring strategic interventions are based on substantive data analysis.
Advantages and Limitations of Interquartile Range
While the interquartile range has significant **advantages**, including resilience to outliers and its clear representation of data spread, it also has **limitations**. IQR does not account for the overall distribution range, which means it can provide an incomplete picture of data variability. For example, if using the IQR alone in a report might lead to missing the presence of extreme values that could impact decision-making. Therefore, it is essential to consider using IQR alongside other statistical measures for comprehensive data analysis.
Examples of Interquartile Range in Real Life
Exploring **examples of interquartile range in real life** can illuminate its practical value. For instance, in educational testing, analyzing student scores using IQR can provide insights into the **spread of achievement** across different student demographics, facilitating targeted interventions. In a retail environment, IQR can help management understand sales data more effectively, allowing strategies to focus on the typical consumer experiences rather than being misled by singular high transactions. Utilizing the IQR in such scenarios demonstrates its utility across various analytical frameworks.
Key Takeaways
- The interquartile range provides a robust measure of data spread, focusing on the central tendency.
- Calculating the IQR involves finding the lower and upper quartiles and using the formula IQR = Q3 – Q1.
- Visualization techniques, such as box plots, effectively communicate the IQR and its significance.
- While the IQR is helpful in major statistical analysis, understanding its limitations is crucial for comprehensive data analysis.
- Practical applications of the IQR extend to various fields like finance, education, and healthcare, aiding in effective decision-making.
FAQ
1. How do you calculate the interquartile range from a dataset?
To calculate the interquartile range from a dataset, first, arrange the data points in ascending order. Next, find the median to split the dataset into two halves. Determine the lower quartile (Q1) as the median of the lower half and the upper quartile (Q3) as the median of the upper half. Finally, compute the IQR using the formula IQR = Q3 – Q1.
2. Why is the interquartile range more reliable than the range?
The interquartile range is more reliable than the range because it focuses on the middle 50% of data, thus reducing the influence of outliers and extreme values. The total range includes the maximum and minimum values, which can misrepresent the spread of the majority of data points, leading to skewed conclusions in data analysis.
3. In what scenarios should I use the interquartile range?
The interquartile range should be used in scenarios where you need to assess the spread of data without the influence of outliers, such as in financial data analysis, education data assessments, or when analyzing performance metrics in various business sectors that may have extreme values affecting average measures.
4. What role does the interquartile range play in data analysis?
The interquartile range plays a crucial role in data analysis by providing insights into the central trend and variability of a dataset, enabling statisticians and researchers to focus on meaningful data representation while identifying outliers that could distort results. It aids in decision-making by facilitating comparisons between different groups or conditions.
5. How can interquartile range assist in identifying outliers?
Interquartile range assists in identifying outliers by serving as a gauge to detect data points that fall significantly outside the typical range of values. Any data points above Q3 + 1.5 * IQR or below Q1 – 1.5 * IQR are flagged as potential outliers, prompting further investigation into their cause and significance in the dataset.
6. Can I visualize the interquartile range easily?
Yes, the interquartile range can be easily visualized through box plots, which graphically represent the minimum, Q1, median (Q2), Q3, and maximum values of a dataset. The box highlight’s the IQR, making it straightforward to interpret when assessing the spread and detecting outliers in the data.
7. What are some practical examples of using the interquartile range?
Some practical examples of using the interquartile range include examining student test scores to evaluate academic performance, analyzing retail sales to understand customer purchasing behavior, or assessing financial metrics to gauge market volatility. These examples reveal the IQR’s versatility across various fields and applications in data evaluation.