How to Properly Cite Multiple Authors in MLA: A Complete 2025 Guide
Citing sources accurately is a crucial skill in academic writing. Understanding how to correctly implement MLA citation formats when dealing with **multiple authors** can significantly enhance the credibility of your work. This comprehensive guide walks you through the steps of citing more than one author according to the latest MLA guidelines.
Understanding MLA Citation for Multiple Authors
The **MLA citation** style provides clear rules for how to cite various sources, especially when they involve multiple authors. The basic premise revolves around giving proper **credit to the original authors**, which not only demonstrates academic integrity but also aids in avoiding plagiarism. You should add citations in both the text (via **in-text citation**) and your **works cited** page to ensure your sources are easily traceable. In this section, we’ll explore the fundamental rules and formats for citing multiple authors effectively.
Citing Two Authors
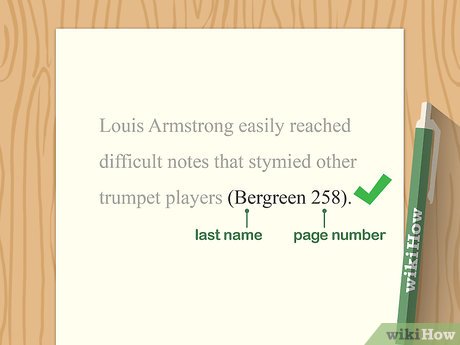
When you have a source with two authors, it is relatively straightforward to cite. In the **in-text citation**, list both authors’ last names in the order they appear on the publication. Format the citation like this: (Smith and Jones 15). On the **works cited** page, the entry should begin with the first author’s name (Last Name, First Name) followed by “and” and the second author’s name (Last Name, First Name). For example:
Smith, John, and Jane Jones. Title of the Book. Publisher, Year.
This structure helps maintain clarity and acknowledges the contributions of both **authors** equally. Correctly applying these citation rules helps ensure **citations in research** support your argument robustly.
Citing Three or Four Authors
When citing three or four authors, you follow a similar structure as with two authors. For the **in-text citation**, include all last names when referencing the text (Smith, Jones, and Brown 45). On the **works cited** page, list the authors’ names in the same order as they appear in the work:
Smith, John, Jane Jones, and Mark Brown. Title of the Book. Publisher, Year.
This method clearly indicates the extent of collaboration within the **multiple authors work**, giving proper recognition to everyone involved in the creation of the piece. Proper attribution reinforces the authority of your research, ensuring **academic integrity**.
Citing More Than Four Authors
In cases where there are four or more **authors**, MLA suggests the use of the first author’s name followed by “et al.” in both **in-text citations** and **works cited** entries. For the in-text, it would appear like this: (Smith et al. 88). In the **works cited** entry, you format it as follows:
Smith, John, et al. Title of the Book. Publisher, Year.
Using “et al.” not only simplifies your citations but also adheres to the MLA guidelines, which are reflected in the **MLA Handbook**. This practice prevents clutter in your citation list while still providing a pathway to the complete list of contributors in the original source, maintaining the **credibility** and **reputation of your references**.
Special Cases in Citing Authors
When working with diverse types of sources such as anthologies, edited collections, or **group authors**, citation might require distinctive handling. This section outlines unique situations and examples that further illustrate how to manage citation challenges.
Citing Group Authors
When referencing a source authored by an organization or group, cite the group as the author. For instance, in-text citation would appear as (American Medical Association 23). According to the MLA requirements, the **works cited** line would be as follows:
American Medical Association. Title of the Book. Publisher, Year.
This method distinctly clarifies the **authority of sources** used in your work, encompassing the full scope of **academic citation ethics**.
Citing Edited Collections and Anthologies
If you are citing a chapter by a specific author in an edited collection or anthology, you will format it differently. The chapter author should be listed first, followed by the editor(s) of the collection. For example:
Doe, Jane. "Title of Chapter." *Title of Anthology*, edited by John Smith and Jane Roe, Publisher, Year, pp. 10-20.
This method allows you to acknowledge not just the chapter authors but also the contributions of the **multiple editors**, which is vital for clarity in **academic writing**.
Online Sources With Multiple Authors
When citing **online sources**, particularly when they involve multiple authors, it’s essential to follow the same principles governing printed sources. Create **parenthetical citations** based on the first author’s name: (Doe et al.), followed by pagination or any accessible data relevant to the source. For digital formats, consider adding access dates as appropriate:
Doe, Jane, et al. "Title of Article." *Title of Website*, Publisher, Date of Publication, URL. Accessed Day Month Year.
Adapting citations for digital media ensures proper attribution and respects the integrity of the information, crucial for **citation consistency** and reliability.
Common Mistakes in Citing Multiple Authors
Despite guidelines, many still struggle with **citation formats**. Below we outline typical errors encountered when citing multiple contributors and how to avoid them, ensuring you meet **discipline-specific requirements** for proper referencing.
Misorder of Authors
A frequent error is the misordering of authors in citations. Always list authors as they appear on the source, respecting the placements for accurate **author name formatting**. Failure to follow this can lead to misunderstandings and misinterpretations of the work’s contributions.
Inconsistent Formatting Across Sources
Ensuring **correctness** in formatting across various references is vital. It’s crucial to maintain a consistent style across your **bibliography management** for a polished appearance. Consider using citation software for **formatting citations** efficiently.
Missing Information in Citations
Another common mistake is missing details such as the publication year, page numbers, or the titles. Each element plays a vital role in **source attribution** and reliability. Always double-check your entries against the **MLA Handbook** or use citation aids when in doubt.
Key Takeaways
- Follow specific MLA guidelines for citing two, three, and four or more authors.
- Use “et al.” for works with four or more authors to simplify citations.
- Acknowledge the authorship of group contributors and proper attribution in edited volumes.
- Avoid common mistakes such as misordering authors or inconsistent formatting for credibility in academic work.
- Utilize citation tools for effective management and correctness in referencing diverse sources.
FAQ
1. How do I cite a source with multiple authors in APA format instead?
In APA format, if a work has up to 20 authors, list them all in the reference. Use “&” before the final author’s name. For works with more than 20 authors, list the first 19, followed by ellipses and the last author’s name. Make sure to follow this structure to maintain continuity within referencing styles.
2. What should I include in the citation for an online article with multiple authors?
For an online article, include all authors’ names presenting them in the proper format followed by the title of the work, website, publication details, and the URL. It’s advisable to include the date accessed for the online reference to reflect the most current information.
3. How can I ensure I don’t plagiarize while using citations?
Properly attributing all direct quotes and paraphrased ideas with accurate citations can prevent plagiarism. It is essential to track the sources as you research and collect necessary bibliographic details to ensure correct referencing.
4. What are the key differences between MLA and APA citation styles?
MLA is commonly used in humanities while APA is employed in social sciences. A major difference is MLA emphasizes authorship while APA focuses on the date of publication. Be mindful of the stylistic nuances in formatting citations as they cater to different academic disciplines.
5. Are there any tools to manage my citations more effectively?
Yes, numerous citation software tools like Zotero, EndNote, and Citation Machine are available that help in organizing and formatting citations. These tools can save time and ensure referring accuracy across multiple authors and various sources.
6. How can I adapt MLA citations for digital sources?
Digital sources need special consideration, such as including a URL and the date of access. Ensure that you adapt the traditional formatting to include necessary digital elements, making it fit the source type while adhering to MLA standards.
7. What is the correct way to cite a secondary source?
To cite a secondary source, mention the original author’s name followed by “qtd. in” and the author of the secondary source. For example: (Smith qtd. in Doe 45). This structure shows respect for the original as well as clarity in your **works cited** list.