How to Properly Quote a Book: Essential Tips for Accurate Referencing in 2025
Understanding the Basics of Quoting
Quoting is a vital skill in academic writing, enabling you to present **direct quotes** from literary works accurately. Understanding how to quote a book properly not only enhances your credibility but also enriches your writing. The significance of accurate quoting lies in maintaining **academic integrity** and providing your readers with substantive evidence that supports your arguments. In this section, we’ll delve into the foundational principles of quoting, focusing on essential components such as **author name**, **page numbers**, and correct usage of **quotation marks**.
The Importance of Quoting Correctly
Quoting correctly ensures that you do not inadvertently engage in plagiarism, which can have serious consequences in academic settings. Whether you’re writing **research papers** or conducting **literary analysis**, it is essential to attribute **source attribution** properly. Ethical practices in quoting, such as maintaining **quotation relevance** and understanding the context of the quotes you use, are essential to foster **scholarly communication**. Besides, improper quoting, including failure to acknowledge sources, can undermine your work’s credibility.
Basic Rules for Creating Accurate Quotes
When citing a book, one must follow certain protocols. Firstly, always include the **publisher information**, along with the **edition information** if it’s applicable, in your reference. When including a quote in your writing, remember to use **quotation marks** to enclose the quoted text. Additionally, do not forget to include an **inline citation** immediately following the quote for clarity on authorship and text location. This method enhances **reader comprehension** concerning where the quote originates.
Citation Styles: APA, MLA, and Chicago
Different academic disciplines often prefer specific citation styles, and familiarity with these is crucial. In this section, we will discuss how to apply the major styles: **APA style**, **MLA style**, and **Chicago style**. Each approach comes with its own set of rules and characteristics that dictate how to handle citations of books correctly.
APA Style Guidelines
The American Psychological Association (APA) format is predominantly used in social sciences. A standard book reference in APA includes the author’s last name, first initial, the publication year, the book’s title, the publisher, and if necessary, the DOI or URL. For example: Smith, J. (2020). The Future of Knowledge. Academic Press. This clearly outlines the attributes like author credibility and publication year, which are crucial for your **bibliography** section in APA style.
MLA Style Characteristics
In contrast, the Modern Language Association (MLA) format is often favored in humanities disciplines. Here, a typical format for a book citation would look like this: Smith, John. The Future of Knowledge. Academic Press, 2020. Note how the **works cited** format emphasizes the author’s full name upfront, followed by the book title in italics. Paying attention to how citations present various elements reinforces **effective quoting** practices.
Chicago Style Insights
The Chicago Manual of Style offers two systems: one for notes and bibliography and another for author-date reference. For instance, in footnote citations, it may look like this: John Smith, *The Future of Knowledge* (New York: Academic Press, 2020), 47. Using footnotes ensures clarity, while the corresponding reference list should accurately reflect all resources for transparent **documentation style** in your scholarly writing.
Integrating Quotes Seamlessly
Integrating quotations into your text can sometimes be challenging. However, learning effective methods can create a smooth flow in your writing while maintaining the **context management** of the quoted material. This section explores different techniques for quoting in a way that resonates with the audience.
Direct vs. Indirect Quotes
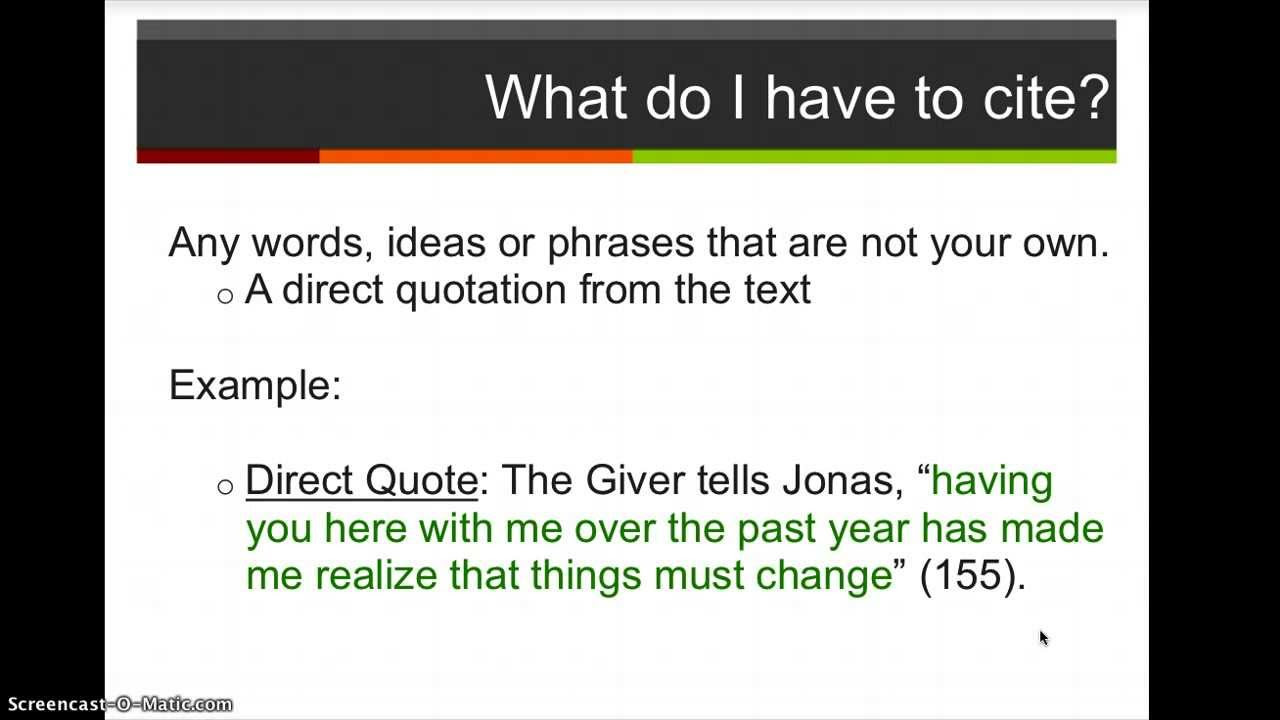
Understanding the difference between **direct quotes** and **indirect quotes** is crucial. Direct quotes should be exact replicas of the original text framed with **quotation marks**, for example, “the whole is greater than the sum of its parts.” Indirect quotes, often paraphrased or summarized, convey ideas from the source without exact wording. Mastering this skill will significantly enhance your **cite sources** capability and simplify your **writing clarity**.
Quote Integration Techniques
When you incorporate quotes, avoid merely dropping them into your text; instead, provide context around the quote. You might write something like: As Jane Doe remarks in her esteemed work, “the essence of writing lies within the power of words.” This technique not only enriches your **writing techniques** but allows your audience to engage more deeply with the material by providing context and clarifying the **quote significance**.
Ensuring Proper Formatting and Ethical Practices
Proper formatting in your quoting practices influences how your writing is perceived. Ethics in quoting are as vital as formatting — adhering to guidelines can maintain your reputation as an esteemed scholar. Here, we’ll examine the attention to detail required for **quintessential referencing**.
Formatting Quotes Appropriately
According to the cited style guidelines, quotes can take various forms. Short quotes, often fewer than four lines, should be included in the text with quotation marks. In contrast, longer quotes, known as block quotes, should be added as a separate paragraph, indented and free from quotation marks. Ensuring correct formatting supports better **reader comprehension** and aligns with **citation best practices**.
Understanding Ethics in Quoting
Using someone else’s words without proper attribution constitutes plagiarism and undermines scholarly discourse. Respecting the original context of quotes involves critically engaging with the material and ensuring your use genuinely represents the author’s intent. This includes considering the significance of the quote and making sure to preserve its meaning, which can enhance your **textual analysis** against the background of your argument.
Key Takeaways
– Understanding the rules around proper quoting is crucial for maintaining academic integrity.
– Familiarity with citation styles like APA, MLA, and Chicago allows you to meet academic standards essential in scholarly writing.
– Integrating quotes effectively in your writing provides clarity and context, enhancing the overall argument.
– Proper formatting and ethical practices are key to ensuring that quoting contributes positively to your academic discourse.
FAQ
1. What are the key elements of a book citation?
A proper book citation includes essential details: the **author name**, **publication year**, **book title**, **publisher information**, and sometimes the **edition information**. This ensures the source is easily traceable for readers.
2. What is the difference between direct and indirect quotes?
A direct quote is an exact reproduction of the original text, framed in **quotation marks**, while an indirect quote paraphrases or summarizes the original ideas without quoting verbatim.
3. How do I choose a citation style?
Your choice of citation style often depends on your academic field. For instance, APA is common in social sciences, while MLA is used primarily in humanities. Understanding your discipline’s norms will inform your selection.
4. What are ethical practices in quoting?
Ethical quoting involves providing necessary attribution for direct and indirect quotes, using the material in context, and representing the author’s original meaning correctly to avoid plagiarism and uphold academic standards.
5. How can I improve my quote integration skills?
To enhance your integration skills, practice contextualizing each quote within your argument, using transition phrases, and ensuring that quotes support your thesis while remaining relevant and coherent.